Dark circles under the eyes are notoriously difficult to treat — largely because they do not all have the same cause. While many people assume that under-eye darkness can be corrected with a single eye cream or lifestyle change, this is rarely the case.
As Dr Derrick Phillips explains, successful treatment depends entirely on matching the solution to the underlying cause. Pigmentation, visible blood vessels, fluid congestion, structural hollowing, muscle prominence, and skin thinning all require different approaches.
This article focuses on how dark circles are treated, once the underlying issue has been properly identified, and why personalised treatment plans consistently deliver the best results for how to get rid of dark circles under the eyes.
Why There Is No Single “Best” Treatment to Get Rid of Dark Circles
One of the most important concepts to understand is that dark circles are rarely caused by a single factor. In many patients, two or three contributing issues exist at the same time. Dr Derrick explains the 5 reasons for dark circles in this article.
For example:
- Pigmentation may be present, but thin skin still allows blood vessels to show through
- Tear trough hollowing may create shadowing, even after pigment is improved
- Puffiness and congestion may worsen vascular darkness despite good skincare
This is why a combination approach, rather than a single treatment, is often required for meaningful, natural-looking improvement.
How to Treat Hyperpigmented Dark Circles
Hyperpigmented dark circles appear brown, grey, or dull and are caused by excess melanin in the under-eye skin. This is particularly common in individuals with darker skin tones, genetic predisposition, or a history of eczema, allergies, or chronic rubbing.
Best Eye Cream Ingredients for Pigmented Dark Circles
Medical-grade eye creams can help regulate pigment production and improve skin quality when used consistently:
- Vitamin C – Brightens skin and supports collagen
- Niacinamide – Reduces inflammation and improves skin barrier function
- Azelaic acid – Helps regulate melanin production
- Liquorice extract – Naturally brightening and anti-inflammatory
- Kojic acid – Targets excess pigmentation
- Tranexamic acid – Reduces pigment signalling pathways
- Low-strength retinoids – Encourage cell turnover and collagen (used cautiously)
While topical products are helpful, they work gradually and require long-term consistency.
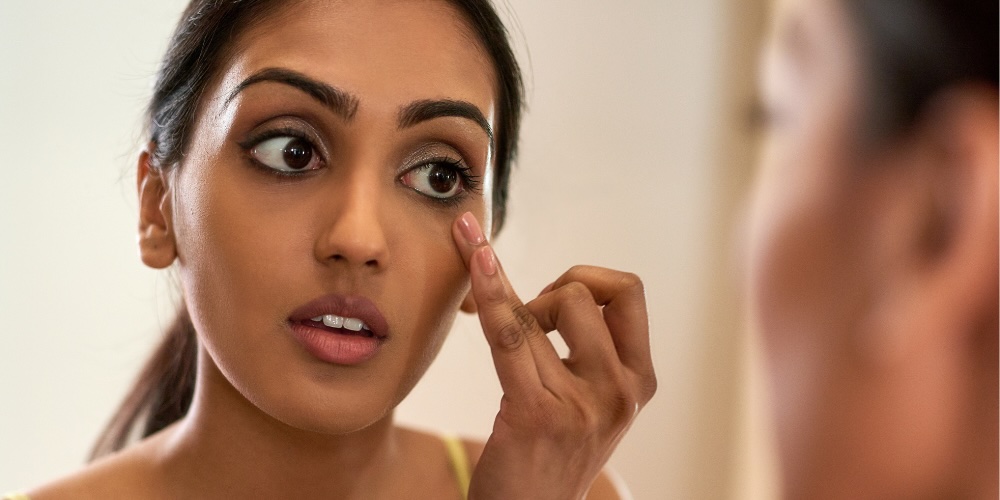

In-Clinic Treatments for Pigmentation
For more established or resistant pigmentation, in-clinic procedures are often required:
- Light chemical peels to gently exfoliate pigmented cells
- Pigment-targeting laser treatments to break down melanin
- Microneedling with brightening serums to improve penetration and skin renewal
- Polynucleotides to enhance skin quality, brightness, and regeneration
Expected results:
Pigmentation improves gradually over weeks to months. The goal is even skin tone and improved brightness rather than aggressive lightening, which can increase irritation and worsen pigment.
Treating Venous & Lymphatic Dark Circles
Venous and lymphatic dark circles appear blue, purple, or reddish and are caused by visible blood vessels, blood pooling, or fluid congestion beneath thin under-eye skin. This type is commonly mistaken for pigmentation.
Topical Support
Topical skincare products help support the skin, but are rarely sufficient alone:
- Caffeine-based eye creams – Constrict blood vessels temporarily
- Retinoids – Gradually thicken the skin, reducing vessel visibility
- Peptides – Improve firmness and support skin structure
Lifestyle Adjustments That Make a Difference for Dark Circles
Congestion-related dark circles often worsen with inflammation and fluid retention. Helpful measures include:
- Treating allergies early
- Improving sleep quality and consistency
- Using cold compresses to reduce swelling
- Reducing salt and alcohol intake
Advanced Treatments
For persistent vascular dark circles, targeted procedures are often most effective:
- Vascular lasers (Nd:YAG, KTP, Pulsed Dye Laser) — selected based on skin type and vessel depth
- Skin boosters or polynucleotides to improve skin thickness and resilience
- Lymphatic drainage techniques to reduce fluid buildup
Expected results:
Reduced blue or purple tones, decreased puffiness, and a brighter, healthier under-eye appearance over time.
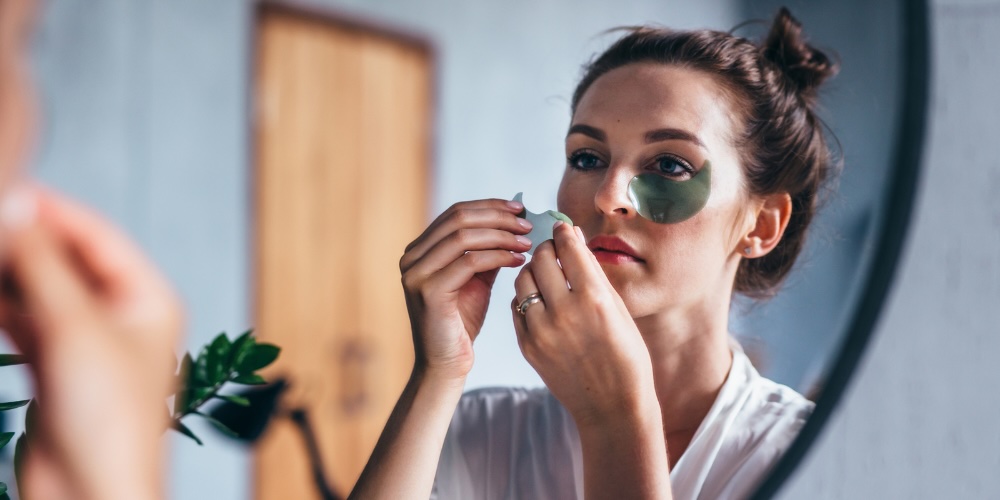

Treating Tear Trough Hollowing (Structural Dark Circles)
Structural hollowing is one of the most common, and most misunderstood causes of dark circles. The darkness is caused by shadowing, not pigmentation.
Eye creams cannot correct structural hollowing.
Gold-Standard Treatments for Tear Troughs
- Tear trough fillers to restore lost volume and support
- Polynucleotides to improve skin quality without adding bulk
- Skin boosters for hydration and elasticity
- Radiofrequency microneedling to tighten and stimulate collagen
- Collagen-stimulating injectables to improve long-term support
Treatment must be conservative and highly individualised to avoid overfilling or unnatural results.
Expected results:
Immediate improvement in shadowing with fillers, followed by progressive improvement in skin quality and under-eye support with regenerative treatments.
Treating Visible Blood Vessels Under Eyes
In individuals with very thin under-eye skin, superficial blood vessels can be clearly visible and contribute to dark circles.
Effective Options
- Vascular lasers (PDL, Nd:YAG, KTP) to target visible vessels
- Skin boosters or polynucleotides to improve skin thickness and quality
- Retinoids to strengthen skin gradually over time
Combination therapy is often required for optimal results.
Daily Maintenance to Prevent Dark Circles
Long-term improvement depends on maintenance and prevention:
- Use SPF 30–50 daily around the eyes
- Avoid rubbing or aggressive cleansing
- Manage allergies promptly
- Maintain hydration and sleep quality
- Treat eczema or dermatitis early
- Use gentle, fragrance-free skincare
- Reduce alcohol and salt intake